CONDITIONS
What is Female Reproductive System?
The female reproductive system includes both internal and external organs. It plays a vital role in hormone production, fertility, menstruation, and sexual activity.
External parts
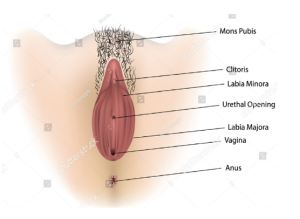
- Labia majora: The labia majora are the outer lips surrounding and protecting the other reproductive organs. The surface of the labia majora, which also has sweat and oil-secreting glands, develops hair growth during puberty.
- Labia minora: The labia minora, or “small lips,” come in different sizes and shapes. They are located inside the labia majora and encircle the openings of the vagina and urethra. The skin of the labia minora is delicate and can become irritated and swollen.
- Clitoris: The clitoris, located near the vaginal entrance, has a sensitive glans and extends internally. It responds to sexual stimulation, becomes swollen, and plays a key role in female orgasm.
- Vaginal opening: The vaginal opening serves as an exit for menstrual blood and facilitates the passage of babies during childbirth.
- Hymen: The hymen is a tissue that covers or partially surrounds the vaginal opening. It forms during development and is typically present at birth.

Internal parts
- Vagina: The vagina is a flexible canal that connects the uterus to the outside of the body. It can expand during childbirth and return to its original size afterward. The vagina is lined with moist mucous membranes.
- Cervix: The cervix is the lowest part of the uterus and has a central opening that allows sperm to enter and menstrual blood to exit. During vaginal childbirth, the cervix dilates to allow the baby to pass through.
- Uterus: The uterus is a muscular, pear-shaped organ located in the pelvis. It consists of two main parts: the cervix, which connects the uterus to the vagina, and the corpus (body), the larger portion of the uterus.
- Ovaries: The ovaries are small, oval-shaped glands on either side of the uterus. They play a crucial role in the reproductive system by producing eggs (ova) and hormones.
- Fallopian tubes: The fallopian tubes are narrow pathways that connect the ovaries to the uterus. The process of fertilization of an egg by sperm cells usually occurs in the fallopian tubes, and the fertilized egg then travels to the uterus, where it is implanted.
Functions
The functions of the female reproductive system include:
- Production of eggs (ova): The ovaries produce and release eggs, also known as ova or oocytes, which are essential for reproduction.
- Ova transport: The system is designed to transport the eggs from the ovaries to the fallopian tubes, where they have the potential to be fertilized.
- Fertilization: In the fallopian tubes, fertilization can occur when sperm meets and penetrates an egg, resulting in conception.
- Implantation and pregnancy: If fertilization occurs, the fertilized egg implants itself in the uterus, where it develops into an embryo and eventually a fetus during pregnancy.
- Menstruation: The female reproductive system undergoes a monthly menstrual cycle, during which the uterus sheds its lining without fertilization.
- Hormone production: The female reproductive system produces hormones that regulate various aspects of reproductive function. The ovaries produce estrogen and progesterone, which control the menstrual cycle, promote the development of secondary sexual characteristics, and support pregnancy.
- Collectively, these functions enable reproduction and the maintenance of the reproductive cycle in females.









