CONDITIONS
What is Urinary System?
The urinary system also called the renal system, removes waste from the blood through urine. It also helps regulate the balance of fluids and electrolytes in the body, as well as controls blood pressure, and maintains the body’s acid-base balance.
Facts about urine
- Normal, healthy urine is a pale straw or clear yellow colour.
- If the urine appears darker yellow or honey-coloured, it often indicates the need for increased water intake.
- A darker, brownish colour of urine may be indicative of a liver problem or severe dehydration.
- The presence of pinkish or red urine may suggest the presence of blood in the urine.
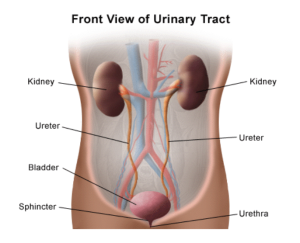
Anatomy
The organs of the urinary system include the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
Kidneys: The kidneys are bean-shaped organs on either side of the spine, below the rib cage. They filter waste products and excess fluid from the blood to produce urine.
Ureters: The ureters are long, muscular tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder. They transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
Bladder: The bladder is a muscular sac that stores urine. It expands as it fills and contracts to empty the urine through the urethra.
Urethra: The urethra is a tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body.
The urinary tract comprises two sphincter muscles, internal and external sphincter muscles. These circular muscles surrounding the bladder’s opening act like a tight rubber band, ensuring a tight closure to prevent any urine leakage.
Functions
- Filtration: The kidneys act as filters, removing waste products, toxins, and excess fluid from the bloodstream. This filtration process helps maintain fluid balance and eliminates harmful substances.
- Urine Production: Blood enters each kidney through numerous small arteries. Blood undergoes filtration within the kidneys separating toxins from essential nutrients. Vitamins, minerals, nutrients, and proteins are reabsorbed into the bloodstream from the filtrate. Waste products and urine then travel through the ureters to reach the bladder, where urine is stored until elimination. Finally, urine is expelled from the body through the urethra during urination.
- Regulation of Fluid and Electrolyte Balance: The urinary system plays a vital role in maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance. The kidneys regulate the levels of water, sodium, potassium, calcium, and other electrolytes to ensure proper functioning of cells and organs.
- Acid-Base Balance: The kidneys help regulate the body’s pH level by controlling the excretion of hydrogen ions and reabsorption of bicarbonate ions, thereby maintaining the acid-base balance.
- Blood Pressure Regulation: The kidneys release hormones that help control blood pressure.









