CONDITIONS
What is Pharynx?
The pharynx, often known as the throat, functions as a part of the respiratory and digestive system. The pharynx is a muscular tube that connects the mouth (oral cavity) and nose to the breathing passages (trachea [windpipe] and lungs) and the esophagus (eating tube). The function of the pharynx is to take in air from the nasal passages as well as food and drink from the mouth. Additionally, the pharyngeal muscles are integral in vital processes such as breathing, swallowing, and speaking.
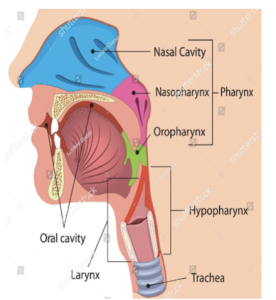
Anatomy
The pharynx is located in the middle region of the neck. It begins at the base of the skull and extends approximately 4.5 inches in length.
The pharynx can be divided into the oropharynx, nasopharynx, and laryngopharynx.
Nasopharynx: This top segment connects to the nose and serves as a pathway for air to pass through.
Oropharynx: The middle part of the throat connects to the mouth. It facilitates the passage of not only air but also food and fluids.
Laryngopharynx (Hypopharynx): Located at the bottom and adjacent to the voice box (larynx), the laryngopharynx regulates the flow of air into the lungs and directs food and liquids into the oesophagus, which leads to the stomach. It acts as a protective mechanism, ensuring food and drink do not enter the trachea while allowing air to reach the lungs for respiration.
In addition, the pharynx includes the eustachian tubes, which connect the middle ear to the back of the nose and throat, and various sets of tonsils that function as part of the immune system. There are three sets of tonsils in the pharynx. The palatine tonsils are the most commonly referred to, found at the back of the throat on either side. The lingual tonsils are situated at the base of the tongue, while the adenoids (pharyngeal tonsils) are located in the nasopharynx, near the opening of the Eustachian tubes. Tonsils help fight off infections by trapping bacteria and viruses that enter the body through the mouth and nose.
Functions
- Passage of Air and Food: The pharynx is a common passageway for air and food. It allows air to pass from the nasal cavity or mouth into the respiratory system, specifically the larynx, and trachea, facilitating breathing. It also enables the passage of food and liquids from the oral cavity into the esophagus, leading to the digestive system.
- Swallowing: Pharyngeal muscles push the food or liquid from the mouth into the esophagus, ensuring the food travels to the stomach for digestion.
- Vocalization and Speech: Laryngopharynx helps in speech and the formation of voice.
- Equalizes pressure in the ear: The eustachian tubes play a role in equalizing air pressure on both sides of the eardrum, maintaining proper ear function.
- Immune Function: The tonsils, part of the pharynx, contribute to the body’s immune system. They help recognize and fight off bacteria and viruses that enter the body through the mouth and nose.









