CONDITIONS
Brain anatomy and functions
The human brain, with an average weight of around 3 pounds, primarily comprises approximately 60% fat. The remaining 40% consists of a combination of water, protein, carbohydrates, and salts. It is protected by the skull and divided into several interconnected regions, each with its unique functions. The brain is a complex organ containing blood vessels, nerves, neurons, and glial cells. It is commonly called the “command center” of the body, allowing us to perceive the world, think, reason, and perform numerous vital functions.
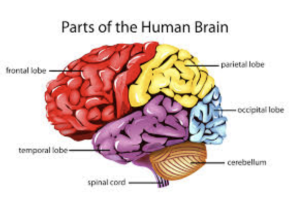
The brain comprises three main parts: the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem.
Cerebrum: The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain and is divided into two hemispheres, each consisting of 4 lobes: the frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes. The cerebrum is responsible for complex thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making tasks. It allows us to process information, learn, and express ourselves.
Cerebellum: Situated at the back of the brain, below the cerebrum. It maintains posture and is responsible for smooth, coordinated movements and balance. It plays a role in learning to ride a bicycle or play a musical instrument.
Brainstem: Located at the base of the brain, the brainstem connects the brain to the spinal cord. It consists of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata. The brainstem regulates essential bodily functions such as breathing, heart rate, and digestion. It also serves as a pathway for sensory and motor signals between the brain and the rest of the body.
Functions of the Brain:
The human brain receives information through the five senses: vision, smell, hearing, touch, and taste. It also processes inputs related to touch, vibration, pain, and temperature from the body, as well as involuntary signals from organs. By interpreting this information, the brain allows us to comprehend and give meaning to our surroundings.
The functions facilitated by the brain include:
- Thinking and decision-making.
- Formation of memories and experiencing emotions.
- Control of voluntary movements, balance, and coordination.
- Perception of sensations, including pain.
- Regulation of automatic behaviours like breathing, heart rate, sleep, and temperature.
- Maintenance of organ function.
- Facilitation of speech and language abilities.
- Activation of the fight-or-flight response during stressful situations.
The human brain is a remarkable masterpiece, containing the very essence of our being. Its complex structure and diverse range of functions profoundly influence our thoughts, emotions, and behaviours.



