CONDITIONS
Throat Cancer
Throat Cancer
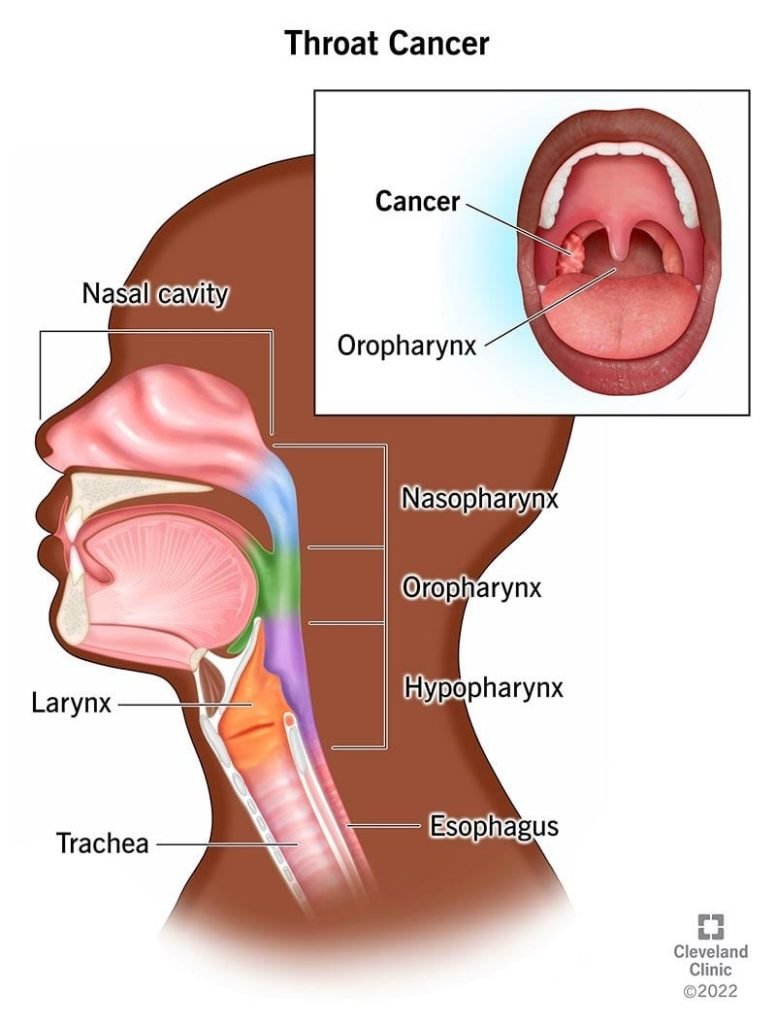
A cancer affecting one or more part of the throat (generally in the middle part of throat (oropharynx) or voice box (larynx) is known as throat cancer.
Approximately 3-6% of all cancers in men is attributed to laryngeal cancer in India. It is the 7th most common cause of cancer in India. Laryngeal cancer (throat cancer) specific risk factors seen in India such as tobacco smoking, alcohol, long-term exposure to indoor air pollution, spicy food, among others.
What are the types of throat cancer?
Depending on the place of origin, cancer is classified and given the following names:
Nasopharyngeal cancer: Begins in part of the throat behind the nose (nasopharynx)
Oropharyngeal cancer: Begins in part of throat right behind the mouth – includes tonsils (oropharynx)
Hypopharyngeal cancer: begins in the lower part of your throat, just above the esophagus and windpipe
Glottic cancer : Begins in the vocal cords.
Supraglottic cancer: Upper portion of the voice box including cancer affecting the epiglottis ( a piece of cartilage blocking food going into windpipe).
Subglottic cancer: Begins in the lower portion of your voice box.
What are the symptoms of throat cancer?
- Changes in the voice where in a person is unable to speak clearly, with hoarseness or voice changes
- Trouble in swallowing
- Breathing difficulties
- Feeling of something stuck in the throat
- Sore throat
- Persistent ear pain
- Headache
- Pain in your ears or neck
- A neck lump or soreness that doesn’t go away.
- Unexplained weight loss
Having these symptoms does not prove that a person has throat cancer. Many times, they are indicators of less severe conditions. Check and consult the doctor if these symptoms last for more than 2 weeks.
What are the risk factors of throat cancer?
Tobacco use: Smoking and chewing tobacco for a long time are the biggest risk for all head, neck cancer, including throat cancer.
Excessive alcohol consumption: More than 2 drinks of alcohol per day for men and 1 drink per day women constitutes a heavy drinker which poses a high risk for throat cancer.
Viral infections such as human papillomavirus (HPV): HPV is often transmitted to through oral sex. There are 100 different types of HPV and around 40 can spread to another person’s mouth, genitals, or throat via oral sex.
A diet with lesser focus on fruits and vegetables
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): Makes stomach acid flow up into the food pipe or the throat.
How is throat cancer diagnosed?
The doctor may examine the throat after getting information about the person’s general health, smoking and drinking habits, and sexual history.
Certain devices and related tests and procedures may be conducted for better examining the throat:
A biopsy: A sample of the tissue is collected to examine them for cancer cells.
Imaging tests such as MRI or CT scan, PET scan and X-rays are conducted to help the doctors find a tumour, its size and the spread of the location. It also helps in staging the cancer. In case of cancer of the oropharynx, the sample may be tested for HPV.
What are the stages of Throat Cancer?
What are the treatment options in throat cancer?
Treatment goals include removing the tumour, preventing the spread of cancer and protecting the ability to swallow and speak as much as possible.
One or more combined treatments may be given as follows:
Radiation therapy:
High-energy rays of radiation are used to kill cancer cells in radiation therapy. Radiation therapy may be the only necessary treatment for throat cancers that are small or those that haven’t spread to the lymph nodes. A combination of chemotherapy or surgery may be done for more-advanced throat cancers.
Surgery:
Surgery may depend on the stages and location of the cancer. The surgical options are as follows:
Surgery for:
- Small throat cancers or throat cancers have not yet spread to lymph nodes: Doctor inserts a hollow endoscope into the throat or voice box while passing special surgical tools or laser through the scope. In many cases, the doctor scrapes off or can vapourize the superficial cancers.
- Removing all or part of the voice box (laryngectomy): The doctor may remove part of the voice box affected by cancer and leave as much voice box as possible to preserve the ability to speak and breath normally as much as possible. Entire voice box may be removed for larger tumours.
- Removing a part of the throat (pharyngectomy): For throat cancers smaller in size, the doctor may remove only small parts of throat during surgery. Removed parts may be reconstructed to help the person swallow food normally.
- Removing cancerous lymph nodes (neck dissection): Surgery to remove some or all the lymph nodes is recommended if the cancer has spread deep within the neck.
Chemotherapy:
Chemotherapy uses chemical substances (drugs) to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy in throat cancer is often used in combination with radiation therapy. However, consult the doctor and understand the side effects before combining therapies as it may increase side effects of both treatments.
Targeted therapy:
Focuses on proteins in the cancer cells. These proteins help in cell growth and multiplication and the treatment kills cancer cells and/or slows their growth.
Immunotherapy:
In cases with spread of throat cancer and where the cancer cannot be removed, immunotherapy medicine called a checkpoint inhibitor may be prescribed. These medicines help the immune system to kill cancer cells by blocking the signals that prevent the body’s defense cells (white blood cells) attacking cancer cells.
How can throat cancer be prevented?
No sure way to avoid throat cancer but certain risk factors may be reduced as follows:
- Quit smoking cigarettes or using any tobacco products. Take external help if smoking cessation is a problem for you.
- Control on the quantity of alcohol consumption.
- Getting vaccinated for HPV and HPV infections because people with a specific HPV type are at higher risk of developing oropharyngeal cancer.
- Develop healthy eating habits such as eating fruits, vegetables with more colour, whole grains and some protein may help in reduction of throat cancer risk. This is because poor nutrition, being overweight, vitamin deficiency is linked to throat cancer.
References
- Bobdey S, Jain A, Balasubramanium G. Epidemiological review of laryngeal cancer: An Indian perspective. Indian J Med Paediatr Oncol. 2015 Jul-Sep;36(3):154-60
- What You Need to Know About Throat Cancer. WebMD. December 2023. https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/throat-cancer-symptoms-treatments
- Laryngeal (larynx) cancer. NHS UK. December 2023. https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/laryngeal-cancer/prevention/
- Throat cancer. December 2023. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/throat-cancer/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20366496
- Throat Cancer. Cleveland Clinic. December 2023. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/23136-throat-cancer#prevention



